Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property ET_Builder_Module_Comments::$et_pb_unique_comments_module_class is deprecated in /home4/readynow/public_html/wp-content/themes/Divi/includes/builder/class-et-builder-element.php on line 1425
ESG Reporting and Disclosure
ESG Reporting and Disclosure Requirements Drive Transparency and Accountability in Global Sustainability and Resilience
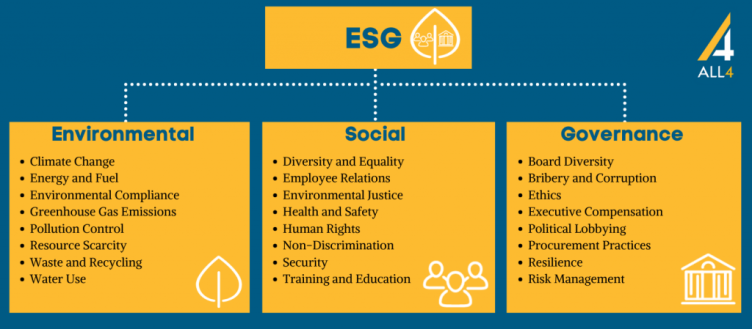
Environmental, Social, and Corporate Governance (ESG) influences the corporate framework that assesses the sustainability and societal impact of any company or organization. Three key factors drive (and measure) the performance and behavior of all enterprises based on environmental, social, and governance factors.
The European Union (EU) sustainability law, enacted earlier this year, aims to enhance risk management and build resilience within the region. Here’s an overview of how the law addresses risk and resilience:
- Risk Identification and Assessment: The EU sustainability law emphasizes the identification and assessment of risks related to climate change, environmental degradation, and other sustainability challenges. It requires companies and financial institutions to conduct thorough risk assessments, considering both physical risks (such as extreme weather events) and transition risks (such as policy changes and market shifts).
- Disclosure and Reporting: The law establishes disclosure requirements for companies, obliging them to disclose information about their exposure to environmental and social risks. This promotes transparency and allows stakeholders to make informed decisions based on the resilience of companies’ operations and strategies.
- Stress Testing and Scenario Analysis: The law encourages stress testing and scenario analysis to evaluate the resilience of companies and financial institutions in the face of sustainability-related risks. By assessing how different potential scenarios, such as increased carbon pricing or stricter regulations, may impact their business, entities can better prepare and adapt their strategies accordingly.
- Financial Sector Resilience: The EU sustainability law recognizes the importance of building resilience within the financial sector. It integrates sustainability considerations into the financial industry, requiring financial institutions to assess and manage ESG risks in their portfolios. This helps to avoid systemic risks and foster a more stable and sustainable financial system.
- Adaptation and Resilience Planning: The law promotes adaptation and resilience planning to address the impacts of climate change and other sustainability challenges. It encourages member states to develop and implement strategies for climate change adaptation, including measures to protect critical infrastructure, manage water resources, and enhance ecosystem resilience.
- Just Transition Fund: In line with the concept of a just transition, the EU sustainability law establishes a Just Transition Fund to support regions, sectors, and communities that are most affected by the transition to a sustainable economy. The fund aims to enhance resilience by providing financial assistance for reskilling, retraining, and the development of new economic activities.
The European Union (EU) sustainability law and the ESG sustainability framework in the United States differ in several ways. Here are some key points of comparison between the two:
- Scope and Integration: The EU sustainability law represents a comprehensive and integrated framework that covers various aspects of sustainability, including climate change mitigation, circular economy, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable finance. It sets binding targets and regulations that apply to all EU member states. In contrast, the United States does not have a single overarching sustainability law but rather a combination of federal and state-level regulations, policies, and initiatives addressing specific aspects of sustainability.
- Climate Change Commitments: The EU sustainability law includes ambitious climate change commitments, aiming for climate neutrality by 2050. It sets binding targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and incorporates these goals into various sectors and policies. In the United States, while there have been efforts at the federal and state levels to address climate change, there is no comprehensive federal legislation that establishes a long-term commitment or specific emissions reduction targets.
- Sustainable Finance: The EU sustainability law places a strong emphasis on integrating sustainability considerations into the financial sector through disclosure requirements, reporting standards, and the promotion of sustainable investments. It establishes a framework for sustainable finance and requires financial institutions to assess and disclose their exposure to environmental and social risks. In the United States, sustainable finance practices and regulations are not as centralized, and efforts are primarily driven by market-based initiatives and voluntary frameworks.
- Approach to Environmental Regulation: The EU generally takes a more prescriptive and regulatory approach to environmental regulation, including sustainability measures. It sets specific standards, targets, and timelines for member states to comply with, often employing a top-down approach. In the United States, environmental regulation is typically more decentralized, with federal regulations serving as a minimum baseline that can be supplemented or exceeded by state-level regulations.
- International Cooperation: The EU has positioned itself as a global leader in sustainability and has actively engaged in international cooperation and agreements, such as the Paris Agreement. It has advocated for ambitious climate goals and sustainability standards on the global stage. The United States has had fluctuations in its approach to international cooperation on sustainability, with varying levels of engagement and commitments depending on the administration in power.
The EU sustainability law represents a more centralized and integrated approach with binding targets, while the United States has a more fragmented landscape with a mix of federal, state, and market-driven initiatives.
By addressing risk and resilience, the EU sustainability law seeks to ensure that companies, financial institutions, and communities are better prepared to manage sustainability challenges effectively. It promotes proactive measures, transparency, and long-term planning to build a resilient and sustainable future within the EU.
To learn more about how ReadyGlobal can help your organization, watch our video or contact us at team@readyglobalnow.com.

0 Comments